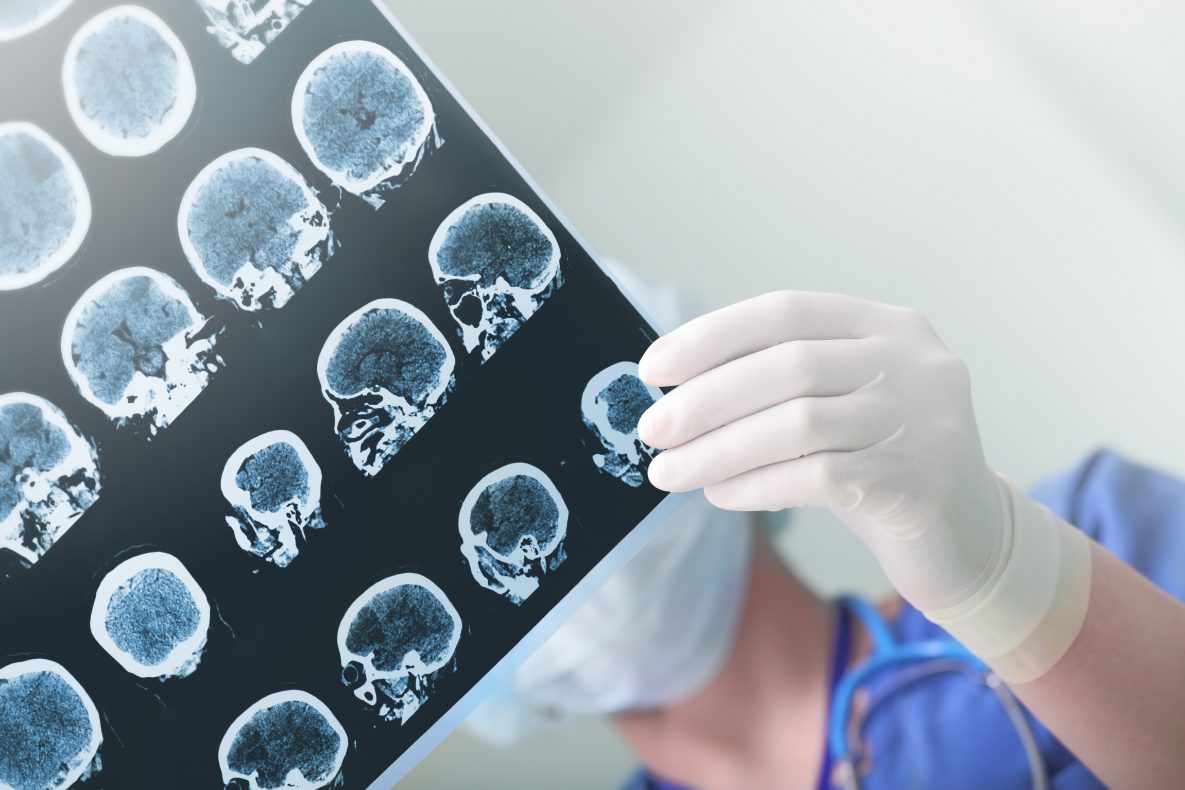
Brain Injuries Leading To Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects approximately 1% of the world’s population. It is characterized by recurrent seizures, brief episodes of involuntary movement, or convulsions.
There are many different types of seizures, and the symptoms can vary from person to person. Seizures can be mild, and some people with epilepsy may not even know they have them. However, seizures can also be severe, leading to loss of consciousness and even death. Contact a brain injury attorney and understand what your legal options are if you suffer epilepsy from traumatic brain injury.
Brain injuries leading to epilepsy
There is no cure for epilepsy, but the condition can be managed with medication. Medication can often control seizures, but not always. Some people with epilepsy may require surgery to remove the area of the brain that is causing the seizures.
Epilepsy is usually diagnosed based on the patient’s medical history and a neurological examination. An electroencephalogram (EEG) may also be used to help diagnose epilepsy. This test records the brain’s electrical activity and can often reveal abnormalities in brain activity associated with seizures.
The link between brain injuries and epilepsy can vary depending on the individual case. However, some possible explanations for how brain injuries can lead to epilepsy include the following:
- Damage to the brain’s electrical system can cause abnormal brain activity and lead to seizures.
- Changes in brain chemistry can make the brain more prone to seizures.
- Damage to the blood vessels in the brain can cause seizures by depriving the brain of oxygen.
- Inflammation of the brain can also lead to seizures.
In many cases, it is difficult to determine exactly how brain injuries lead to epilepsy, as multiple factors can be involved.
Diagnosis of Brain Injuries
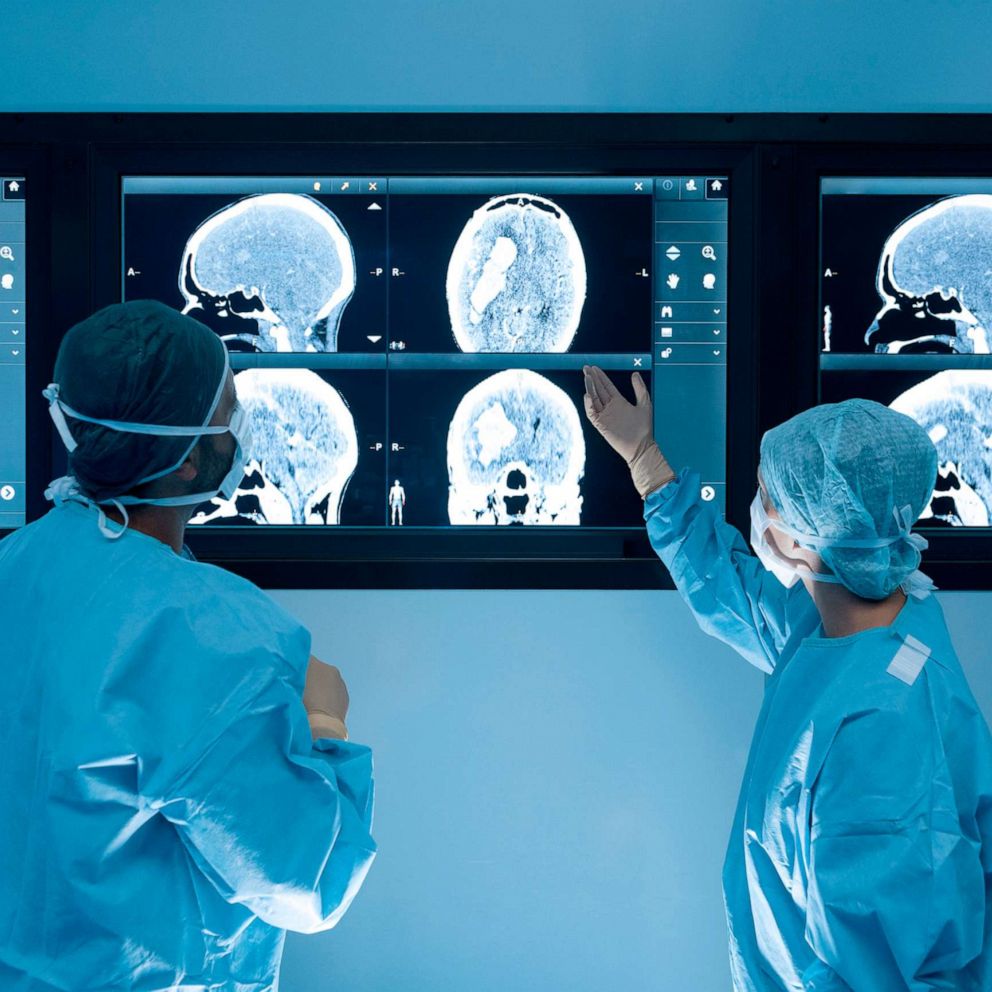
Diagnosis of a brain injury that has the potential to lead to epilepsy can be difficult and time-consuming. In many cases there may not be any obvious signs or symptoms, so the diagnosis usually involves both medical history and physical exams. Imaging techniques such as computerized tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, positron emission tomography (PET) scans and electroencephalograms (EEGs) can help to identify brain injuries that are more likely to cause seizures. Medical tests such as blood tests may also be conducted.
After a physical examination and other tests have been completed, the doctor may diagnose a brain injury if something abnormal is found in any of these imaging techniques or tests. In many cases, the cause of the injury will remain uncertain even after all testing is complete. If this happens, the doctor may recommend further observation in order to determine whether symptoms will develop over time or if epilepsy is likely to occur as result of a brain injury.
Treatment for epilepsy
No such treatment is possible to cure epilepsy, but one can reduce the risks and occurrence of epilepsy if one maintains proper medication, diet, etc.
1. Medication
The most common treatment used in dealing with epilepsy is medication. Medications are typically used in the treatment of epilepsy that is resistant to surgery. The drugs combined with other therapy have significantly reduced the frequency of seizures and made them more tolerable.
The most common medications used in treating epilepsy are Phenobarbital, Phenytoin, Primidone, etc.
2. Side effects of medications
The side effects of these drugs vary and can be mild, moderate, or severe. If a person experiences side effects that are not tolerable, then they may switch to another drug. The most common side effects of epilepsy medications are:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Double vision
- Headache
